The Morinaga Group Environmental Policy clearly states that we will deepen our understanding of biodiversity and strive to maintain and conserve biodiversity and protect ecosystems. We will make efforts to understand our corporate activities’ dependence and impact on natural capital, and work to maintain and conserve it.
| Area | Details |
|---|---|
| Governance |
The Morinaga Group’s analysis of risks and opportunities, target setting, and progress monitoring concerning sustainability initiatives is deliberated by the Sustainability Committee, which is chaired by the Representative Director, President. Findings are then reported to the Board of Directors, which also supervises the status of activities.
|
| Risk Management | The Morinaga Group’s Total Risk Management Committee, which is chaired by the Representative Director, President, identifies risks, evaluates the severity, reviews countermeasures against these risks, monitors progress, and manages and addresses risks appropriately. Climate change and other risks are managed and addressed appropriately as management risks by the same committee. In addition, the TCFD/TNFD Subcommittee conducts reviews in line with the TCFD/TNFD recommendations, with the results deliberated by the Sustainability Committee. The details of discussions held by both committees are reported to the Board of Directors, which oversees the progress of risk management. Based on the above, management conducts business operations after carrying out appropriate oversight of company-wide risks. |
Using the TNFD framework and the LEAP approach*1 advocated by the TNFD as a reference, we analyzed the Group’s dependence and impacts on natural capital, risks, and opportunities.
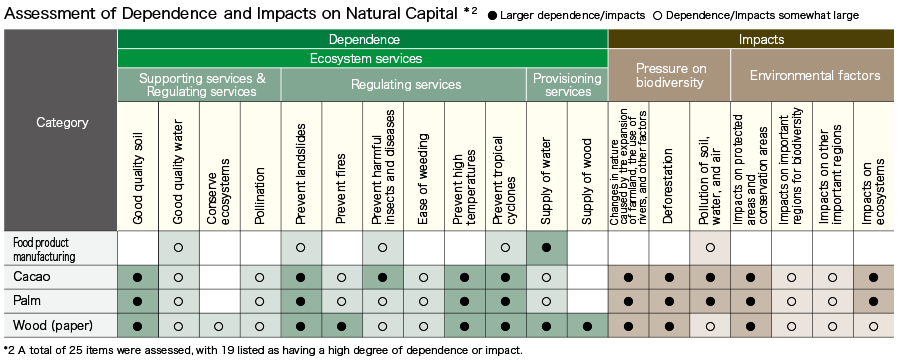
The Group recognizes its dependence and impacts on natural capital associated with corporate business activities as shown in the figure 1 below. In addition, we confirmed the dependence and impacts of the Group’s main business of food product manufacturing, and the Group’s main raw materials, such as cacao, palm, and wood (paper). The figure 2 below shows the results of our assessment on 25 items̶16 dependent items and nine impact items̶using an external tool.
The production of food products is particularly dependent on the supply of water. We understand that the production of cacao, palm, and wood (paper) depends on many forms of natural capital such as good quality soil, water, and climate adjustment, and that the expansion of farmland and deforestation might affect biodiversity.
Figure 1
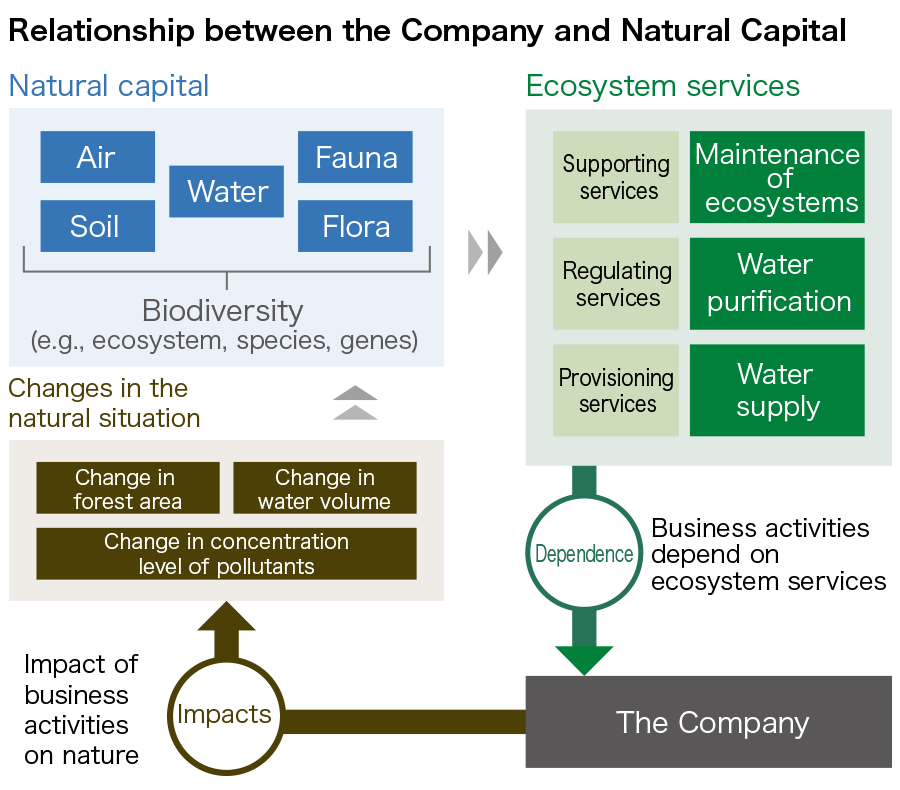
Figure 2
Below, there is a summary of the risks and opportunities and responses to them. We will continuously deepen our understanding of the situation of natural capital and strive to maintain and conserve natural capital and biodiversity.
| Category | Subcategory | Risk factors | Impact on operations | Importance | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Risks |
Chronic | Ecosystem infrastructure and adjustment/changes in services |
Increased raw materials costs and development costs due to deterioration of soil and water quality and decreased yields of agricultural crops caused by increased occurrences of pests and diseases |
Large | ● Promote raw materials procurement in consideration of the environment in line with the Procurement Policy and Supplier Guidelines ● Promote initiatives to achieve the target of 100% sustainable procurement of cacao beans, palm oil, and paper raw materials by 2030*3 ● Cooperate with suppliers and enhance communication to respond to risks ● Purchase raw materials from multiple suppliers (or multiple sites) |
| Changes in rainfall patterns and extreme changes in weather patterns |
Rising raw material and development costs due to poor crop quality and reduced yield caused by changes in weather patterns and frequent occurrences of extreme weather | Large | |||
| Transition Risks |
Laws and Regulations |
Changes in laws and regulations related to the maintenance of ecosystems |
Increased raw materials costs due to higher demand for materials certified as considering the environment | Medium | |
| Stricter nature-related reporting obligations | Increased reporting costs | Medium | ● Continuous information collection ● Continuous response to nature-related risks |
||
| Markets | Changes in consumer behavior | Increased environmental awareness among consumers leads to a decline in sales due to consumer defection from products that have been slow to respond to the environment and a decrease in the adoption of such products by retailers | Large | ● Promote raw materials procurement in consideration of the environment in line with the Procurement Policy and Supplier Guidelines |
| Category | Opportunity factors | Impact on operations | Importance | Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resource Efficiency | Development and use of efficient production and distribution processes |
Declining manufacturing and transport costs due to development of efficient manufacturing and distribution processes | Large | ● Promote efficient production activities by rebuilding the production system and creating smart factories*4 ●Promote initiatives aimed at 70% reduction in food loss and waste by 2030*5 ● Establish more efficient system/transport logistics and deliveries with fewer environmental impacts |
| Products and Medium Services |
Changes in consumer preferences | Increased demand for environmentally considered products amid increased environmental awareness among consumers, including Generation Z |
Large | ● Promote initiatives to achieve the target of 100% sustainable procurement of cacao beans, palm oil, and paper raw materials by 2030*3 ● Develop environmentally considered products |
| Resilience | Substitution/ Diversification of resources |
Increasing capacity of operations under various conditions from review of substitution/diversification of raw materials | Large | ●Consider substitution and diversification of raw materials based on climate change risks |
| Increased trust in supply chain and fewer opportunity loss due to formulation of resilience plan (BCP) | Large | ●Continuously review BCP for natural disasters and promote BCM |